|
GSAS uses the term "histogram" to refer to a diffraction data set. A histogram can also be a set of "soft constraints," e.g. a set of target parameters, such as bond distances, that the model will also try to fit. GSAS can fit a model to up to 99 histograms simultaneously, although the majority of refinements done in GSAS use a single histogram or at most only a few histograms. GSAS can use single crystal or powder diffraction data, either neutron or x-ray. For neutron powder diffraction data, the data can be obtained from either time-of-flight (TOF) or constant wavelength (CW) instruments. GSAS can use x-ray data from synchrotron, laboratory alpha-1,2, and even energy-dispersive x-ray instruments. Two files are needed to load a powder diffraction histogram. The first is a file containing the powder diffraction data, often called a GSAS raw data file (often using the extension .RAW, .GSA or .GSAS) and the second file is an instrument parameter file (.INS or .INST) that defines what type of data is included in the raw file (x-ray/neutron, CW/TOF/ED, etc.) as well as starting values for the diffractometer constants and peak shape parameters. There are a number of available formats for the raw data files and types of records in the instrument parameter file; this information is defined in the GSAS documentation. Note that raw data files can contain more than one set of data and that an instrument parameter file can contain more than one set of parameters. This feature is rarely used, with the exception of TOF instrumentation, where detectors are grouped into banks and the results for each bank are included in a single file. Software for translating diffraction data into a format accepted by GSAS is available at most user facilities or may possibly be found via web searching. Appropriate instrument parameter files can usually be provided by the instrument scientist at a user facility or prototypes can be found in the GSAS distribution files. This web page demonstrates how the alumina powder diffraction data are now added to the experiment file. For this tutorial exercise, a special instrument parameter file that has peak shape values narrower than the actual instrument is provided. The tutorial would be less challenging if the appropriate instrument parameter file is used. |
|
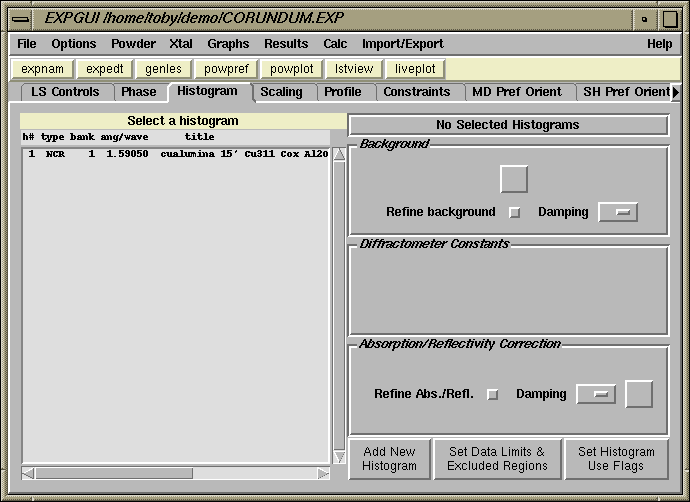
The Histogram panel is selected by clicking on the Histogram tab, as is shown below. In this case, no data has been defined, as can be determined by the absence of entries in the histogram selection box, in the upper left. The "Add New Histogram" button, at the lower right, is used to add [additional] powder diffraction data sets to the refinement, as will be demonstrated in this page. The histogram panel is used to modify various parameters associated with each set of diffraction data, for example the diffractometer constants (such as wavelength), the background function and terms.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The "Usable data limit" sets the maximum range of data to be used in fitting. This is usually determined by plotting the data to see where no further peaks are present. This can be done here with the GSAS RAWPLOT program. For this exercise, change the defaulted value (the entire data range) to 155 degrees, to exclude a single very broad high-angle peak. The press the "Add" button in the lower left. |
|
After the "Add" button is pressed, the EXPGUI program runs a GSAS program, EXPTOOL, that actually adds the data reference to the experiment. If an error occurs, this result is shown. If no error occurs, the histogram panel is redisplayed, but this time a histogram appears in the upper left, as seen below.
|

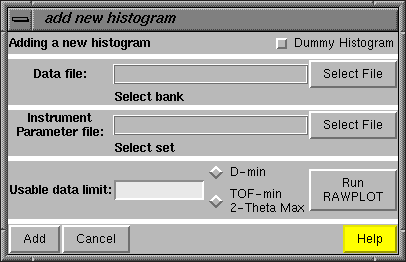 Pressing the "Add New Histogram" button causes the "add new histogram" window, shown to the right, to be displayed. The entries on this window are usually considered from top to bottom. The "Dummy Histogram" option is used to simulate powder diffraction data, and is not used in this tutorial example. So the next item of interest is to select a data file. This is done by pressing the upper of the two "Select File" buttons.
Pressing the "Add New Histogram" button causes the "add new histogram" window, shown to the right, to be displayed. The entries on this window are usually considered from top to bottom. The "Dummy Histogram" option is used to simulate powder diffraction data, and is not used in this tutorial example. So the next item of interest is to select a data file. This is done by pressing the upper of the two "Select File" buttons.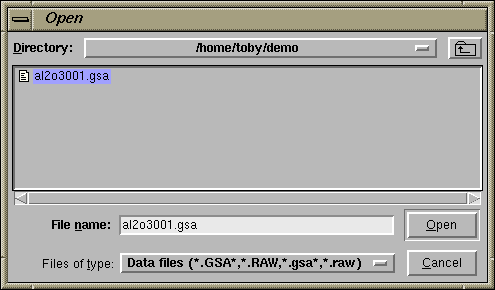 Pressing the "Select File" button creates a file open window, such as the one to the right (or slightly different in appearance in windows). Select the input file for this exercise, the file you
Pressing the "Select File" button creates a file open window, such as the one to the right (or slightly different in appearance in windows). Select the input file for this exercise, the file you 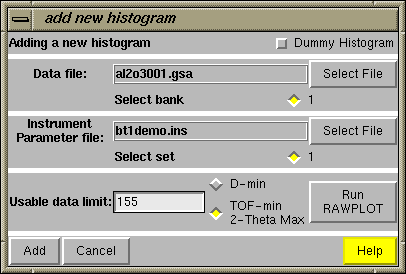 Selecting the raw data file in the open window causes the al2o3001.gsa file to be loaded into the upper box on the "add new histogram" window. This file is scanned to and check mark entries are created for each bank in the file. The al2o3001.gsa file also defines a default instrument parameter file, which is the bt1demo.ins that was
Selecting the raw data file in the open window causes the al2o3001.gsa file to be loaded into the upper box on the "add new histogram" window. This file is scanned to and check mark entries are created for each bank in the file. The al2o3001.gsa file also defines a default instrument parameter file, which is the bt1demo.ins that was