The original MIT news release by Raleigh McElvery can be read here.
Despite its minute size, a single cell contains billions of molecules that bustle around and bind to one another, carrying out vital functions. The human genome encodes about 20,000 proteins, most of which interact with partner proteins to mediate upwards of 400,000 distinct interactions. These partners don’t just latch onto one another haphazardly; they only bind to very specific companions that they must recognize inside the crowded cell. If they create the wrong pairings — or even the right pairings at the wrong place or wrong time — cancer or other diseases can ensue. Scientists are hard at work investigating these protein-protein relationships, in order to understand how they work, and potentially create drugs that disrupt or mimic them to treat disease.
The average human protein is composed of approximately 400 building blocks called amino acids, which are strung together and folded into a complex 3D structure. Within this long string of building blocks, some proteins contain stretches of four to six amino acids called short linear motifs (SLiMs), which mediate protein-protein interactions. Despite their simplicity and small size, SLiMs and their binding partners facilitate key cellular processes. However, it’s been historically difficult to devise experiments to probe how SLiMs recognize their specific binding partners.
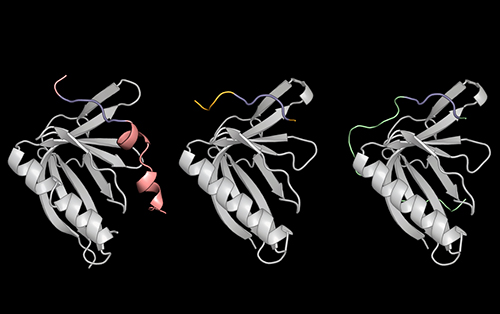
To address this problem, a group led by Theresa Hwang Ph.D. ’21, designed a screening method to understand how SLiMs selectively bind to certain proteins, and even distinguish between those with similar structures. Using the detailed information they gleaned from studying these interactions, including x-ray crystallography data (Fig. 1) obtained at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Advanced Photon Source (APS), a DOE Office of Science user facility at Argonne National Laboratory, the researchers created their own synthetic molecule capable of binding extremely tightly to a protein called ENAH, which is implicated in cancer metastasis. The team shared their findings in a pair of eLife studies, one published on Dec. 2, 2021 [1], and the other published Jan. 25, 2022 [2].
“The ability to test hundreds of thousands of potential SLiMs for binding provides a powerful tool to explore why proteins prefer specific SLiM partners over others,” says Amy Keating, professor of biology and biological engineering and the senior author on both studies. “As we gain an understanding of the tricks that a protein uses to select its partners, we can apply these in protein design to make our own binders to modulate protein function for research or therapeutic purposes.”
Most existing screens for SLiMs simply select for short, tight binders, while neglecting SLiMs that don’t grip their partner proteins quite as strongly. To survey SLiMs with a wide range of binding affinities, Keating, Hwang, and their colleagues developed their own screen called MassTitr.
The researchers also suspected that the amino acids on either side of the SLiM’s core four-to-six amino acid sequence might play an underappreciated role in binding. To test their theory, they used MassTitr to screen the human proteome in longer chunks comprised of 36 amino acids, in order to see which “extended” SLiMs would associate with the protein ENAH.
ENAH, sometimes referred to as Mena, helps cells to move. This ability to migrate is critical for healthy cells, but cancer cells can co-opt it to spread. Scientists have found that reducing the amount of ENAH decreases the cancer cell’s ability to invade other tissues — suggesting that formulating drugs to disrupt this protein and its interactions could treat cancer.
Thanks to MassTitr, the team identified 33 SLiM-containing proteins that bound to ENAH — 19 of which are potentially novel binding partners. They also discovered three distinct patterns of amino acids flanking core SLiM sequences that helped the SLiMs bind even tighter to ENAH. Of these extended SLiMs, one found in a protein called PCARE bound to ENAH with the highest known affinity of any SLiM to date.
Next, the researchers combined a computer program called dTERMen with x-ray crystallography data from studies at the Northeastern Collaborative Access Team 24-ID-E x-ray beamline at the APS in order understand how and why PCARE binds to ENAH over ENAH’s two nearly identical sister proteins (VASP and EVL). Hwang and her colleagues saw that the amino acids flanking PCARE’s core SliM caused ENAH to change shape slightly when the two made contact, allowing the binding sites to latch onto one another. VASP and EVL, by contrast, could not undergo this structural change, so the PCARE SliM did not bind to either of them as tightly.
Inspired by this unique interaction, Hwang designed her own protein that bound to ENAH with unprecedented affinity and specificity. “It was exciting that we were able to come up with such a specific binder,” she says. “This work lays the foundation for designing synthetic molecules with the potential to disrupt protein-protein interactions that cause disease — or to help scientists learn more about ENAH and other SLiM-binding proteins.”
Ylva Ivarsson, a professor of biochemistry at Uppsala University who was not involved with the study, says that understanding how proteins find their binding partners is a question of fundamental importance to cell function and regulation. The two eLife studies, she explains, show that extended SLiMs play an underappreciated role in determining the affinity and specificity of these binding interactions.
“The studies shed light on the idea that context matters and provide a screening strategy for a variety of context-dependent binding interactions,” she says. “Hwang and co-authors have created valuable tools for dissecting the cellular function of proteins and their binding partners. Their approach could even inspire ENAH-specific inhibitors for therapeutic purposes.”
Hwang’s biggest takeaway from the project is that things are not always as they seem: even short, simple protein segments can play complex roles in the cell. As she puts it: “We should really appreciate SLiMs more.”
See: [1] Theresa Hwang1, Sara S Parker2, Samantha M Hill2, Meucci W Ilunga1, Robert A. Grant1, Ghassan Mouneimne2, Amy E. Keating1*, “A distributed residue network permits conformational binding specificity in a conserved family of actin remodelers,” eLife 10, e70601 (2021). DOI:10. 7554/eLife.70601
Author affiliations: 1Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2University of Arizona Cancer Center
Correspondence: * keating@mit.edu
This project was supported by National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) award R01 GM129007 to A.E.K. and by NCI award R01 CA196885-01 to G.M. Part of this work has been supported by Koch Institute NCI Cancer Center (Core) Support Grant (CCSG) P30-CA14051. The Northeastern Collaborative Access Team beamlines are funded by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences from the National Institutes of Health (P30 GM124165). The Eiger 16 M detector on the 24-ID- E beamline is funded by an NIH-ORIP HEI grant (S10OD021527). T.H. was partially supported by NIGMS T32 GM007287 and a fellowship from the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research. This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract DE-AC02-06CH11357.
[2] Theresa Hwang1, Sara S Parker2, Samantha M Hill2, Robert A Grant1, Meucci W Ilunga1, Venkatesh Sivaraman1, Ghassan Mouneimne2, and Amy E Keating1*, “Native proline-rich motifs exploit sequence context to target actin-remodeling Ena/VASP protein ENAH,” eLife11, e70680 (2022). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.70680
Author affiliations: 1Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2University of Arizona
Correspondence: *keating@mit.edu
This project was supported by National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) award R01 GM129007 to A.E.K., NCI award R01 CA196885-01 to G.M., and the Koch Institute Support (core) Grant P30-CA14051 from the National Cancer Institute. The Northeastern Collaborative Access Team beamlines are funded by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences from the National Institutes of Health (P30 GM124165). The Eiger 16 M detector on the 24-ID- E beamline is funded by an NIH-ORIP HEI grant (S10OD021527). T.H. was partially supported by NIGMS T32 GM007287 and a fellowship from the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research. This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under contract DE-AC02- 06CH11357.
The U.S. Department of Energy's APS at Argonne National Laboratory is one of the world’s most productive x-ray light source facilities. Each year, the APS provides high-brightness x-ray beams to a diverse community of more than 5,000 researchers in materials science, chemistry, condensed matter physics, the life and environmental sciences, and applied research. Researchers using the APS produce over 2,000 publications each year detailing impactful discoveries, and solve more vital biological protein structures than users of any other x-ray light source research facility. APS x-rays are ideally suited for explorations of materials and biological structures; elemental distribution; chemical, magnetic, electronic states; and a wide range of technologically important engineering systems from batteries to fuel injector sprays, all of which are the foundations of our nation’s economic, technological, and physical well-being.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC, for the U.S. DOE Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit the Office of Science website.
