The original Michigan State University press release can be read here.
In a paper published in Nature Communications, based on research at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Advanced Photon Source (APS), scientists in Susannah Dorfman’s Experimental Mineralogy Lab at Michigan State University (MSU) redefined the conditions under which carbonates can exist in the Earth’s lower mantle, adding to our understanding of the deep carbon cycle and the Earth’s evolution.
“The circulation of carbon and minerals from the surface of the Earth through subduction to the base of the Earth’s mantle has been happening for billions of years,” said Dorfman, assistant professor in the MSU Department of Earth and Environmental Science (EES) in the College of Natural Science and co-author of the paper. “Our lab asks, ‘how can we use experiments to predict what it looks like and to follow it chemically?’”
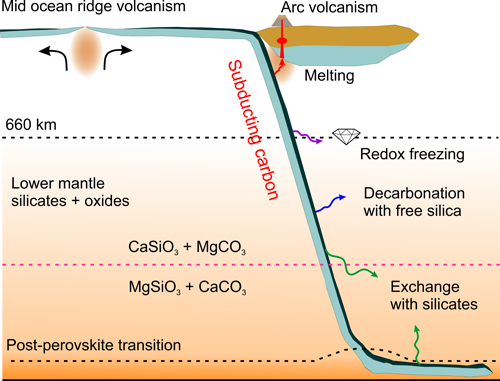
During subduction, surface carbonates (think limestone and coral skeletons) hitch a ride on cold slabs of rock diving under Earth’s crust through tectonic motion fueled by the mantle’s heat. Some carbonates melt and are spewed back into the atmosphere by volcanoes. Some travel further down and are pressed into diamonds.
But what about the carbonates that make it even deeper, toward the Earth’s core-mantle boundary almost 1,800 miles below the surface? A place so deep it is impossible to recover a sample?
Dorfman’s previous research showed that some carbonates could indeed escape being melted or turned into diamonds in a hot, oxygen-poor environment like the core-mantle boundary, but no one knew what form they would take in a real rock until now.
In the current study, Dorfman and co-author Mingda Lv, a fifth-year EES doctoral student, conducted highly complex experiments to synthesize mantle rock and illuminate the fate of those deeply subducted carbonates for the first time.
“For this project, we wanted to know how carbonate would coexist with the majority of mantle silicates when subducted to the lower mantle,” Lv explained. “We designed the experiments to extend the pressure and temperature conditions on these minerals to high regimes, simulating conditions at the core-mantle boundary of the Earth.”
“What we were interested in is, when is carbon not diamond?” added Dorfman.
Cooking up rock under the extreme temperature and pressure conditions of Earth’s lower mantle goes far beyond the ability of your kitchen’s pressure cooker. Their experiments required a device made of material with the highest-pressure tolerance of any substance on Earth—diamonds.
“The diamond anvil cell, even though it is something you can hold in your hand, gives us the very highest pressures in any lab without using explosions,” Dorfman said. “All of what we know about what goes on in the center of planets is dependent on this device.”
Dorfman and Lv successfully assembled thin carbonate and silicate discs like a sandwich between the two diamonds of the diamond anvil cell. Then, they squeezed the discs together like a mineral panini and used powerful lasers to heat them to soaring temperatures of up to 4,500°F.
The result was something no one thought possible, a synthesized form of highly pressurized calcium carbonate rock that could exist in lower mantle conditions.
“Before this study, the idea was that you should never have calcium carbonate in the deep Earth, but only in a shallow environment where it hasn’t gotten down to great depths,” Dorfman said. “Our experiments show that toward the base of the mantle, the chemical reaction changes direction and swaps minerals like partners in square dancing—the magnesium and calcium swap their carbonate and silicate partners producing calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate.” Fig. 1
The size of their newly synthesized rock was only the width of a human hair, and the individual crystals comprising the rock were up to 1,000 times smaller. To read between the diamonds, Dorfman and Lv needed the sharpest knife and brightest light they could find.
Working at the GeoSoilEnviroCARS x-ray beamline 13-ID-D at the Argonne National Laboratory APS, the team reproduced high-temperature conditions found at the mantle by using a double-sided ytterbium fiber laser-heating system and then employed the extremely powerful, high-brightness APS x-rays to probe sample properties in situ at extreme conditions with the high-resolution angle-dispersive x-ray diffraction technique before, during, and after laser heating. Then, with the help of collaborators at the Institute of Earth Physics of Paris and the University of Michigan’s Center for Materials Characterization, they used ion beams to slice the new rock into cross-sections.
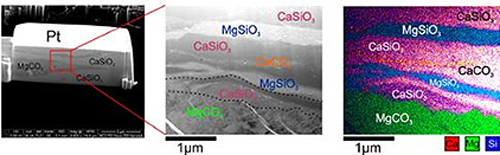
Finally, using the state-of-the-art electron microscopy techniques at MSU’s Center for Advanced Microscopy, they successfully characterized the elemental distribution of their recovered samples (Fig. 2).
“Without these labs, we would never have been able to directly observe what is going on in our experiments,” Lv said. “Our collaboration with these facilities is a highlight of the study.”
“We know that a vast majority of the Earth’s carbon isn’t up in the atmosphere, it’s in the interior, but our guess as to how much and where depend mostly on measurements of chemical reactions,” Dorfman added. “Mingda Lv’s work shows that calcium carbonate can be stable in mantle conditions and provides a new mechanism to take into account when we make models of the carbon cycle inside the Earth.”
See: Mingda Lv1, Susannah M. Dorfman1, James Badro2, Stephan Borensztajn2, Eran Greenberg3‡, and Vitali B. Prakapenka3, “Reversal of carbonate-silicate cation exchange in cold slabs in Earth’s lower mantle,” Nat. Commun. 12, 1712 (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21761-9
Author affiliations: 1Michigan State University, 2Institut de physique du globe de Paris, 3The University of Chicago ‡Present address: Soreq Nuclear Research Center (NRC)
Correspondence: *lyumingd@msu.edu, **dorfman3@msu.edu
This work was supported by new faculty startup funding from Michigan State University, the Sloan Foundation’s Deep Carbon Observatory Grant G-2017-9954, and National Science Foundation (NSF) grant EAR-1751664 to S.M.D. Parts of this work were supported by IPGP multidisciplinary program PARI, and by Region Île-de-France SESAME Grant no. 12015908. GeoSoilEnviroCARS is supported by NSF grant EAR-1634415. This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357.
© Michigan State University
The U.S. Department of Energy's APS is one of the world’s most productive x-ray light source facilities. Each year, the APS provides high-brightness x-ray beams to a diverse community of more than 5,000 researchers in materials science, chemistry, condensed matter physics, the life and environmental sciences, and applied research. Researchers using the APS produce over 2,000 publications each year detailing impactful discoveries, and solve more vital biological protein structures than users of any other x-ray light source research facility. APS x-rays are ideally suited for explorations of materials and biological structures; elemental distribution; chemical, magnetic, electronic states; and a wide range of technologically important engineering systems from batteries to fuel injector sprays, all of which are the foundations of our nation’s economic, technological, and physical well-being.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC, for the U.S. DOE Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit the Office of Science website.
