The original National Institutes of Health press release can be read here.
Research teams from the National Institutes of Health and abroad, with an assist from high-brightness x-rays produced at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Advanced Photon Source (APS), have identified the first inhibitor of an enzyme long thought to be a potential drug target for fighting disease-causing parasites and bacteria. The teams, led by NIH's National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) and University of Tokyo scientists, sorted through more than 1 trillion small protein fragments called cyclic peptides to uncover two that could shut down the enzyme. The finding, reported April 3, 2017 in Nature Communications, could set the stage for the potential development of new types of antimicrobial drugs.
NCATS' expertise in early stage, pre-clinical molecule discovery helped the teams find potential drug candidates that could have implications for millions of people worldwide.
"The work is an excellent demonstration of how NCATS delivers on its mission to provide improvements in translational processes," said Anton Simeonov, Ph.D., scientific director, NCATS Division of Pre-Clinical Innovation. "Scientists have shown that a therapeutic target, previously considered undruggable by pharmaceutical companies, is actually druggable through a non-traditional therapeutic agent."
The target enzyme, cofactor-independent phosphoglycerate mutase (iPGM), is found in both parasites and bacteria. Several types of parasitic roundworms have iPGM, including Brugia malayi and Onchocerca volvulus, which infect roughly 150 million people living mostly in tropical regions. These parasites can cause devastating infectious diseases, such as river blindness. The enzyme also is found in bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, which can cause the hospital-borne infection MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), and Bacillus anthracis, which causes anthrax.
"Several infectious organisms are potentially susceptible to an iPGM inhibitor," said co-corresponding author James Inglese, Ph.D., director, NCATS Assay Development and Screening Technology Laboratory. "The team dubbed the inhibitor peptides 'ipglycermides,' which represent a powerful class of iPGM inhibitors. In theory, such a drug could become a broad spectrum anti-parasitic and anti-bacterial treatment."
Current anti-parasitic drugs, such as ivermectin, mainly work on the early larval stages of the worm. Such a treatment must be given annually or semiannually for as long as a decade. For years, scientists have tried to find a more effective drug that also worked against the adult worm and the later stages of infection. Earlier studies by Inglese's collaborators at New England Biolabs in Ipswich, Massachusetts, showed that iPGM is one of many essential enzymes the roundworm needs to survive. It is part of a common biological process called glycolysis, which helps make energy for cells. While the same important process occurs in human cells, it relies on a different form of the enzyme. As a result, a drug that targets iPGM and kills the roundworm would likely leave the human counterpart alone. Such a drug might work on all life stages of the worm, and the infection could possibly be treated acutely, akin to an antibiotic. However, their previous attempts at finding a compound to block the enzyme have failed.
Enzymes are proteins that jumpstart chemical reactions. Most enzymes have pocket-shaped "active sites" into which a molecule fits, and on which the enzyme acts. Small molecule drugs can fit in active sites and prevent, or inhibit, the enzyme from doing its biological job. But iPGM and other similar enzymes are different. iPGM has a short-lived, temporary active site, making it practically impossible to find a small molecule drug that can block the enzyme.
Because of the enzyme's unusual design, the NCATS-led team sought a different type of drug than the typical small molecule drugs. Inglese collaborated with co-corresponding author Hiroaki Suga, at the University of Tokyo, to build a library mixture of more than 1 trillion small peptides. The team went one step further, adding an amino acid to the peptides to create ring-shaped cyclic peptides, which the scientists hypothesized would have the needed shape and structure to attach to the enzyme surface and disable the enzyme.
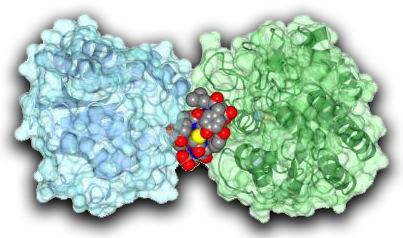
The researchers sifted repeatedly through the cyclic peptides to find which would stick most tightly to the enzyme. They found two cyclic peptides that both bound tightly to only the iPGM enzyme and also shut down its activity.
The team subsequently worked with structural biologists at the University of Kansas, Lawrence, to carry our x-ray diffraction studies at the Industrial Macromolecular Crystallography Association Center for Advancing Therapeutics (IMCA-CAT) 17-ID-B beamline at the Argonne National Laboratory APS in order to determine the structure of the iPGM-cyclic peptide arrangement, showing how the peptide prevented the enzyme from working properly. "The cyclic peptide has amazingly tight and selective affinity for iPGM, like an antibody," Inglese said.
(The APS is an Office of Science user facility.)
The group's next steps will be to find ways for cyclic peptides to enter cells. "If we can find ways to put cyclic peptides into cells, then this would open up new targets that small molecule drugs have a difficult time addressing," Inglese said. "Ipglycermides represent a fertile yet uncultivated landscape between small molecule drugs and protein biologics."
Researchers from other institutions, including the National Institute of Standards and Technology (Gaithersburg, Maryland), and the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (part of NIH) also participated in the work.
See: Hao Yu, Patricia Dranchak, Zhiru Li, Ryan MacArthur, Matthew S. Munson, Nurjahan Mehzabeen, Nathan J. Baird, Kevin P. Battaile, David Ross, Scott Lovell, Clotilde K.S. Carlow, Hiroaki Suga, and James Inglese*, “Macrocycle peptides delineate locked-open inhibition mechanism for microorganism phosphoglycerate mutases,” Nat. Commun. 8, 14932 (2017). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14932
Correspondence: *jinglese@mail.nih.gov
This research was supported in part (Z1ATR000247-01) by the Intramural Research Program of the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, NIH (J.I.), and in part by the AMED Basic Science and Platform Technology Program for Innovative Biological Medicine (JST-CREST Molecular Technologies) to H.S. Use of the University of Kansas Protein Structure Laboratory was supported by a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (P30GM110761) from the National Institutes of Health. Use of the IMCA-CAT beamline 17-ID at the Advanced Photon Source was supported by the companies of the Industrial Macromolecular Crystallography Association through a contract with Hauptman-Woodward Medical Research Institute. This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. DOE Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02- 06CH11357.
See also: “Fighting Parasitic Infections: Promise in Cyclic Peptides,” NIH Director’s Blog, by Dr. Francis Collins, April 11, 2017.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit the Office of Science website.