Unraveling the complexities of spin-orbital coupling could someday lead to new high-temperature superconductors and workable quantum computers via an elusive phase of matter called a “quantum spin liquid.” Two groups of researchers utilizing x-ray beamlines at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory are delving into the new physics required to develop just such a material.
The electrons that surround an atom’s nucleus usually possess independent degrees of freedom including orbital momentum and spin. But in certain circumstances, these two entangle, resulting in a composite state. Spin-orbital coupling is not a new phenomenon, but the way it alters the behavior of novel materials is not yet well-understood.
Because these materials have great fundamental and technological promise, deciphering the effects of spin-orbital coupling is a research priority. Iridates are being explored now because they are one of very few systems that have been predicted to behave as quantum spin liquids, and because tools were developed that can reliably study the spin-orbital coupling. One such tool is resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS), which is available to users of the APS.
X-ray measurements of spin-orbit coupling in iridium oxide materials show exciting new results, which are the basis of two papers recently published back-to-back in Physical Review Letters. In one paper, a group led by Xuerong Liu from Brookhaven National Laboratory and composed of scientists at Brookhaven National Laboratory, Argonne National Laboratory, IFW Dresden, and the University of Kentucky, used RIXS on X-ray Science Division (XSD) beamline 9-ID to study electronic excitations and deduce the wave function of the iridium electrons. They reported that the model commonly used to describe electronic structure in iridium oxides is flawed.
The other paper, authored by a group led by Jungho Kim of the APS and including other researchers at Argonne, IFW Dresden, and the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research in Stuttgart reported finding novel magnetic behavior in a different iridium oxide compound.
The shape of the electron cloud surrounding an atom affects how that atom interacts with nearby atoms. This shape changes when the orbitals are entangled with spin. The researchers looked at the electronic structure of Sr3CuIrO6, a compound in which the iridium atoms are surrounded by oxygen atoms in a slightly distorted octahedron.
Such a system is typically modeled by assuming that the octahedron is perfectly regular and thus the orbital degree of freedom is being quenched in certain ways. If the shape is not perfect, then the layout of the electron cloud is deformed, but previous research groups have assumed that minor irregularities made little difference and could be ignored. In this case, the structure of Sr3CuIrO6 is close to the ideal.
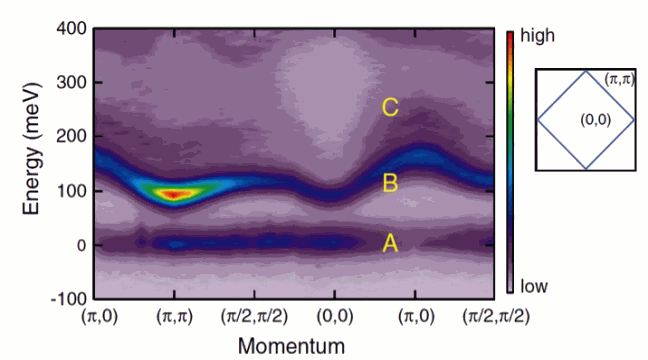
When the Brookhaven-led group gathered data on the actual structure, however, they found that the irregularity makes a noticeable and important change to the wave function, which thus deforms the orbitals of the active electrons, as shown in the graphic. When the spin couples to the orbitals, the effect cannot be ignored.
“Although the fundamental physics for spin-orbit coupling is clear,” said Liu, “our work suggests that the ideal case is not true in real materials.”
The study allows researchers to describe such systems more realistically by including distortion as a parameter in models. And, because the orbital shape determines how each electron interacts with its neighbors, this has important consequences on the magnetism in these solids.
The spin-orbital coupling in another iridate compound, Sr3Ir2O7, results in a magnetic behavior not seen before. The research carried out by the Argonne-led team showed that the coupled states in this material behave – on an atomic scale – just like classically sized bar magnets, with two magnetic poles, although the mechanism from which it arises is different. Typical assumptions that charge interactions dominate over spin interactions are not correct in this case, in which the spin-orbit coupling is strong. This could be the basis for creating new materials.
“This coupling between pairs of spins is extremely weak,” said co-author B. J. Kim of the Argonne Materials Science Division. “There was no hope of seeing it with conventional materials.” They probed the material utilizing XSD beamline 30-ID at the APS.
Both groups investigated the spin-orbital coupling in their iridate compounds utilizing RIXS. In both cases, the novel behavior due to spin-orbital coupling could be observed clearly in the iridium compounds because iridium is a large atom and the effects of the coupling are larger than for smaller atoms, and also because RIXS can measure the subtle effects of spin-orbital coupling.
“RIXS is similar to neutron scattering because both probe the dynamics in a system,” said Liu, “but RIXS has the advantage that it couples to both the electron orbitals and spin. Neutron scattering doesn’t ‘see’ the charge part of the electrons.”
“While neutron scatterings is good for low energies,” Jungho Kim said, “RIXS is appropriate for looking at the high energies of the electrons.” The technique can also operate on very small amounts of material. – Yvonne Carts-Powell
See: X. Liu1*, Vamshi M. Katukuri2, L. Hozoi2, Wei-Guo Yin1, M. P. M. Dean1, M. H. Upton3, Jungho Kim3, D. Casa3, A. Said3, T. Gog3, T. F. Qi4, G. Cao4, A. M. Tsvelik1, Jeroen van den Brink2, and J. P. Hill1, “Testing the Validity of the Strong Spin-Orbit-Coupling Limit for Octahedrally Coordinated Iridate Compounds in a Model System Sr3CuIrO6“ Phys. Rev. Lett 109, 157401 (2012).
Author affiliations: 1Brookhaven National Laboratory, 2IFW Dresden, 3Argonne National Laboratory, 4University of Kentucky
Correspondence: *xliu@bnl.gov
The work at Brookhaven was supported by the U. S. Department of Energy DOE Division of Materials Science, under Contract No. DE-AC02-98CH10886. The work at IFW Dresden was supported by the Computational Materials and Chemical Sciences Network program of the Division of Materials Science and Engineering, U. S. DOE through Grant No. DE-SC0007091. Use of the Advanced Photon Source was supported by the U. S. DOE Office of Science under Contract No. DE-AC02- 06CH11357. T. F.Q and G. C. were supported by the National Science Foundation through Grant No. DMR-0856234.
See: Jungho Kim1, A. H. Said1, D. Casa1, M. H. Upton1, T. Gog1, M. Daghofer2, G. Jackeli3, J. van den Brink2, G. Khaliullin3, and B. J. Kim2*, “Large Spin-Wave Energy Gap for the Bilayer Iridate Sr3Ir2O7: Evidence for Enhanced Dipole-like Interactions near the Mott Metal-Insulator Transition,” Phys. Rev. Lett 109, 157402 (2012).
Author affiliations: 1Argonne National Laboratory, 2IFW Dresden, 3Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research
Correspondence: *bjkim@anl.gov
Work in the Materials Science Division and the use of the Advanced Photon Source at the Argonne National Laboratory was supported by the U.S. DOE under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. G. J. acknowledges support from GNSF/ST09-447. M.D. acknowledges support from the DFG (Emmy-Noether program).
The Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory is one of five national synchrotron radiation light sources supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science to carry out applied and basic research to understand, predict, and ultimately control matter and energy at the electronic, atomic, and molecular levels, provide the foundations for new energy technologies, and support DOE missions in energy, environment, and national security. To learn more about the Office of Science x-ray user facilities, visit http://science.energy.gov/user-facilities/basic-energy-sciences/.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.